Search Market Research Report
Waste To Energy Market

Waste To Energy Market By Technology (Biochemical, Thermal, and Others), and By Region - Global Industry Insights, Growth, Size, Share, Comparative Analysis, Trends and Forecast 2022 – 2028
Industry Insights
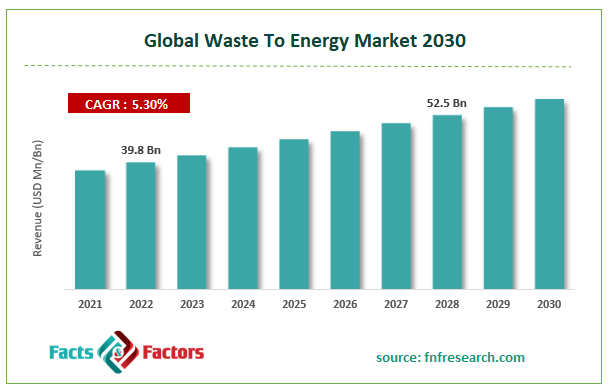
[215+ Pages Report] According to Facts and Factors, the global waste to energy market was worth USD 39.8 billion and is anticipated to be worth USD 52.5 billion by 2028, expanding at a CAGR of 5.3% over the projected period. This market report provides a thorough examination of the industry. The report examines key aspects, developments, drivers, constraints, the market segments, and the competitive landscape in depth.
 Market Overview
Market Overview
Waste to energy (WtE) or energy from waste (EfW) is a method of energy recovery that is used to generate energy in the form of heat and light through the principal treatment of waste. Most of these techniques aid in the direct generation of heat or electricity via thermal combustion or the generation of a combustible fuel commodity such as synthetic fuels, methane, methanol, and ethanol, among others.
 COVID-19 Impact:
COVID-19 Impact:
The COVID-19 outbreak has impacted economic growth by delaying the operational processes of key sectors like recycling waste and energy generation. The industries are closed tight or operate under restricted conditions, such as fewer employees and shorter working hours. Many countries, including the United States, Spain, China, Poland, Austria, India, Korea, Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy, declared a state of emergency.
The pandemic caused a labor and raw material shortage in the recycling and energy generation industries. The magnitude of the impact may force the closure of some waste-to-energy producers. Manufacturers' production was halted due to a labor shortage. As a result, production output was reduced, resulting in economic losses.
 Growth Drivers
Growth Drivers
- Heat and power generation from waste to drive market growth
Waste to energy is an effective and sustainable waste treatment method that generates heat that can be used to generate electricity. These waste-to-energy plants can reduce waste by 94 to 95% while keeping it out of landfills. These plants provide numerous advantages and destroy contaminated medical disposals and other harmful garbage. Waste to energy technology has several advantages, including the production of heat & power, effective waste management, the reduction of waste, the prevention of the production of methane gas & hazardous greenhouse gases, and greater control over sound & odor during the process of decomposition, limited pollution, no groundwater contamination, effectiveness in metal recycling, and others. All of these advantages are expected to drive the global waste to energy market demand during the forecast period.
 Restraints
Restraints
- The high installation costs of waste to energy plants will limit market growth
The construction of waste-to-energy plants, particularly incineration plants, is expensive because it includes the cost of necessary infrastructure, operational costs, waste disposal & segregation costs, and other expenses. Furthermore, trained personnel and dedicated employees are required to manage incinerator plants because they require regular maintenance, which is expected to impede market growth during the forecast period.
 Opportunities
Opportunities
- Waste to energy has the potential to replace coal, which is expected to create massive opportunities
Using municipal solid waste to generate energy for energy plants is a more efficient and cost-effective option than coal power plants. The use of coal to generate electricity transmits harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and hydrogen chloride, as well as toxic trace elements such as mercury, lead, and cadmium. On average, waste to energy plants can burn up to 320 million tons of garbage per year, which is then used to generate electricity. This reduces the demand for coal plants and other fossil fuels, which are nonrenewable energy sources. Furthermore, because these plants trap dioxin, they prevent the emission of hazardous compounds such as dioxin, which is expected to create excellent growth opportunities for the global waste to energy market during the forecast period.
 Segmentation Analysis
Segmentation Analysis
The global waste to energy market is segmented on the basis of technology and region.
By technology, the market is divided into biochemical, thermal, and others. The thermal method involves the high-temperature recyclable materials of energy from MSW. Thermal technology encompasses a variety of processes, including combustion or incineration, gasification, and pyrolysis. The main distinction between these technological innovations is the O2 and temperature associated with the process that gives rise to the conversion to final products, water, and CO2, or to intermediate useful products.
During the forecast period, the incineration segment is expected to grow at a rapid pace. Increased waste generation around the world significantly drives global demand for incineration processes. Because incinerators can treat all types of waste, this method is far superior to other thermal waste treatment techniques.
 Report Scope
Report Scope
Report Attribute |
Details |
Market Size in 2021 |
USD 39.8 Billion |
Projected Market Size in 2028 |
USD 52.5 Billion |
CAGR Growth Rate |
5.3% CAGR |
Base Year |
2021 |
Forecast Years |
2022-2028 |
Key Market Players |
China Everbright International Limited, Ramboll Group A/S, Hitachi Zosen Inova AG, Wheelabrator Technologies Inc, Veolia, Xcel Energy Inc., Covanta Holding Corporation, Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc., Suez, Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC., and Others |
Key Segment |
By Technology, and By Region |
Major Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa |
Purchase Options |
Request customized purchase options to meet your research needs. Explore purchase options |
 Regional Landscape
Regional Landscape
- The market in the Asia Pacific region is expected to expand rapidly
Among the regions in the global waste to the energy market, Asia Pacific was worth USD 17.5 billion in 2020 and is expected to be worth USD 26 billion by 2028, with a CAGR of 5.3%. The increasing population and the influx of immigrants to cities result in a large amount of waste being produced on a daily basis. Furthermore, the COVID-19 outbreak has seriously affected countries such as China and India, resulting in panicked buying of goods, an increase in single-use products, and the deposition of large amounts of medical waste, which contributes to plastic pollution.
As a result, Shenzhen, one of China's largest megacities, has built the world's largest waste-to-energy plant, capable of processing up to 5,500 tons of waste per day. Furthermore, China operates over 305 waste-to-energy plants, which efficiently manage waste and produce power. Similarly, Veolia, a waste management and energy services company in India, manages more than 91 waste to energy centers that treat municipal solid waste and produce electricity.
 Recent Development
Recent Development
- January 2021: The Indian state-controlled oil firm (IOC) and the North Delhi Municipal Corporation (NDMC) have collaborated to establish a waste-to-energy plant (WtE) at the NDMC's Ranikhera landfill site in New Delhi.
- October 2021: The waste-to-energy plant in Kapuluppada, Andhra Pradesh, India, has been officially opened. The plant's capacity is approximately 15 MW, and it is entitled to receive 900 to 1000 tonnes of waste per day from the Greater Visakhapatnam Municipal Corporation.
 Competitive Landscape
Competitive Landscape
Some of the key global waste to energy market players are
- China Everbright International Limited
- Ramboll Group A/S
- Hitachi Zosen Inova AG
- Wheelabrator Technologies Inc
- Veolia
- Xcel Energy Inc.
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises Inc.
- Suez
- Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC.
The global waste to energy market is segmented as follows;
 By Technology Segment Analysis
By Technology Segment Analysis
- Biochemical
- Thermal
- Others
 By Regional Segment Analysis
By Regional Segment Analysis
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Nordic Countries
- Denmark
- Sweden
- Norway
- Benelux Union
- Belgium
- The Netherlands
- Luxembourg
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- South Korea
- Southeast Asia
- Indonesia
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Singapore
- Rest of Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- The Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Egypt
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Industry Major Market Players
- China Everbright International Limited
- Ramboll Group A/S
- Hitachi Zosen Inova AG
- Wheelabrator Technologies Inc
- Veolia
- Xcel Energy Inc.
- Covanta Holding Corporation
- Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises Inc.
- Suez
- Abu Dhabi National Energy Company PJSC
Frequently Asked Questions

Copyright © 2024 - 2025, All Rights Reserved, Facts and Factors


