Search Market Research Report
Zinc Ion Battery Market Size, Share Global Analysis Report, 2025 – 2034

Zinc Ion Battery Market Size, Share, Growth Analysis Report By Product Type (Zinc-Mn Battery, Zinc-Chloride Battery, Zinc-Carbon Battery, Zinc-Silver Battery, Zinc-Nickel Battery, and Zinc-Air Battery), By End-Use Industry (Consumer Electronics, LED Lighting, Automotive, and Others), And By Region - Global Industry Insights, Overview, Comprehensive Analysis, Trends, Statistical Research, Market Intelligence, Historical Data and Forecast 2025 – 2034
Industry Insights
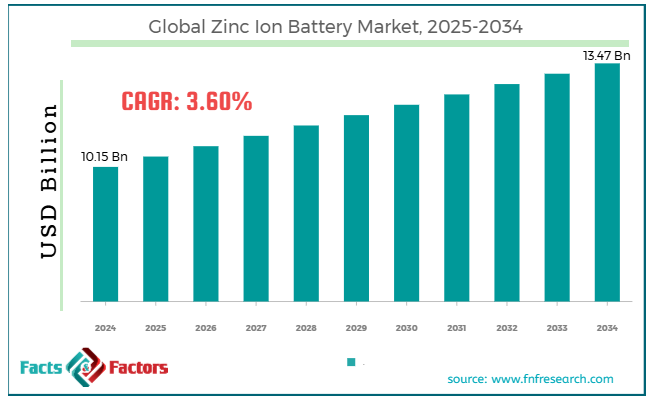
[221+ Pages Report] According to Facts & Factors, the global zinc ion battery market size was worth around USD 10.15 billion in 2024 and is predicted to grow to around USD 13.47 billion by 2034, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of roughly 3.60% between 2025 and 2034.
 Market Overview
Market Overview
Zinc-ion batteries are a favorable alternative to conventional lithium-ion batteries, offering ecological friendliness, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced safety. These batteries utilize zinc as the anode, which is readily available, stable, and non-toxic in aqueous electrolytes, thereby reducing the risk of thermal runaway and fire.
Zinc-ion technology has gained massive popularity due to its long lifespan, high energy density, and potential for minimal manufacturing costs. The global zinc ion battery market is progressing at a notable pace due to the rising demand for safe battery technology, low cost, and the abundance of zinc, as well as the emerging renewable energy sector. Zinc-ion batteries are thermally stable and non-flammable due to their aqueous electrolytes. This leads to rising demand in various sectors, prioritizing optimal safety, which encompasses both electric mobility and stationary storage.
Zinc is the fourth most commonly used metal and is readily available worldwide. This makes zinc-ion batteries highly cost-effective compared to lithium-ion equivalents, which rely on costly, geopolitically sensitive elements such as nickel and cobalt.
Moreover, as wind and solar installations continue to grow, the demand for efficient and safe grid storage solutions is escalating. Zinc-ion batteries are considered suitable for these uses due to their stable charging and discharge performance, as well as their long lifespan.
Nevertheless, the global market faces challenges due to the low energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries, a short lifecycle under certain conditions, and a lack of consumer awareness. Zinc batteries currently have a low energy density, which limits their use in high-performance applications, such as drones or electric vehicles, where weight and speed are crucial.
Despite numerous advancements, zinc-ion batteries may encounter issues like reduced performance and dendrite formation after multiple cycles, particularly with poor electrolyte stability. Additionally, OEMs and end-users are still familiar with lead-acid and lithium-ion technologies, resulting in slow market penetration and adoption of new substitutes, such as zinc-ion.
However, the global zinc ion battery industry is projected to experience significant growth due to the replacement of lead-acid batteries, the deployment of decentralized telecom towers and microgrids, as well as applications in aerospace and the military. Zinc-ion batteries may serve as high-performance and environmentally friendly substitutes for lead-acid batteries in UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) systems, automation SLI systems, and backup power batteries.
Moreover, developing countries with off-grid telecom towers or inconsistent grid access need safe, durable, and low-maintenance power sources, increasing the suitability of zinc-ion batteries. Additionally, zinc-ion batteries are highly preferred for defense applications, including mobile power packs and radar systems.
 Key Insights:
Key Insights:
- As per the analysis shared by our research analyst, the global zinc ion battery market is estimated to grow annually at a CAGR of around 3.60% over the forecast period (2025-2034)
- In terms of revenue, the global zinc ion battery market size was valued at around USD 10.15 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 13.47 billion by 2034.
- The zinc ion battery market is projected to grow significantly due to the advancement of the renewable energy sector, the low cost and abundance of zinc, as well as the recycling and environmental benefits.
- Based on product type, the zinc-mn battery segment is expected to lead the market, while the zinc-air battery segment is expected to grow considerably.
- Based on end-use industry, the consumer electronics segment is expected to lead the market, surpassing the LED lighting segment.
- Based on region, Asia Pacific is projected to dominate the global market during the estimated period, followed by North America.
 Growth Drivers
Growth Drivers
- Growing demand for LED lighting and consumer electronics boosts market growth
Although lithium-ion batteries lead the way in portable devices, zinc-ion batteries are being explored for LED lighting and consumer electronics, particularly in developing countries where safety, affordability, and recyclability are prioritized.
Philips Lighting associated with ZincFive Incorporation in February 2025. This partnership aims to integrate zinc-ion battery backup into off-grid LED lighting solutions in Sub-Saharan Africa, highlighting safer disposal and lower operational costs.
This adoption is supported by stringent regulations aimed at phasing out harmful battery chemistries, particularly in consumer electronic applications, which is expected to impact the growth of the zinc ion battery market.
- Green energy mandates and supportive government policies considerably fuel the market growth
Governments worldwide are actively encouraging advancements in battery technology beyond lithium-ion to enhance energy resilience and reduce reliance on critical minerals. Zinc-ion technology supports green industrial policies due to its recyclability, absence of conflict minerals, and minimal ecological footprint.
For instance, the European Union introduced its 'Beyond Lithium' initiative in 2024 under the Horizon Europe program. The initiative has distributed over €80 million to support research for non-lithium batteries, including zinc-ion solutions.
 Restraints
Restraints
- Heavy competition from emerging alternative chemistries hampers the market progress
The zinc ion battery industry faces intense competition from next-generation battery solutions, including lithium-sulfur, solid-state lithium-ion, redox flow batteries, and sodium-ion batteries. Most of these substitutes are obtaining significant funding and developing speedily toward commercialization.
In addition, redox flow batteries, such as iron-based systems, are highly preferred for long-term grid storage due to their exceptional scalability and unique cycle life. ESS Incorporation obtained a USD 50 million DOE loan in 2024 to expand its iron flow production in the United States, supporting the zinc ion opportunity domain.
 Opportunities
Opportunities
- Mounting demand for long-duration grid energy storage propels the market growth
With the growing adoption of renewable energy, grid operators actively need long-lasting energy storage technologies to alleviate the intermittency of wind and solar power. Zinc-ion batteries, with their enhanced calendar life and high depth-of-discharge, are progressing as viable competitors in the category.
Urban Electric Power declared a 50 MWh zinc-ion power storage system in Texas in March 2025. This was done in association with ERCOT, dedicated to stabilizing the grid during extreme weather conditions. This project is anticipated to operate for over a decade with minimal degradation, demonstrating the viability of zinc ions for utility-scale distribution.
- Commercial and industrial backup power systems contribute to the industry's growth
With the rising demand for UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supplies) and backup battery systems in industries such as telecom, healthcare, manufacturing, and data centers, zinc-ion batteries are gaining prominence as a vital alternative to lithium-ion and lead-acid technologies.
In addition, the TRAI has recently advised the use of zinc-ion batteries for mobile applications in Tier 3 and Tier 2 cities, citing improved resistance to vandalism, enhanced ecological performance, and reduced theft compared to lead-acid systems.
 Challenges
Challenges
- Investor hesitation and financing restrictions restrict the growth of market
Institutional investors and venture capital remain cautious about zinc ion solutions, primarily due to their limited track records, high technical risks, and competing substitute chemistries.
Besides, several investors believe that zinc-ion batteries are restricted to low-end or niche markets, such as microgrids and backup systems, which decreases their attraction for increased growth capabilities. Without government-led procurement or significant private-public associations, it will be challenging for zinc ion firms to gain the capital required for factory buildouts and R&D.
 Report Scope
Report Scope
Report Attribute |
Details |
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 10.15 Billion |
Projected Market Size in 2034 |
USD 13.47 Billion |
CAGR Growth Rate |
3.60% CAGR |
Base Year |
2024 |
Forecast Years |
2025-2034 |
Key Market Players |
Zinc8 Energy Solutions, Urban Electric Power, Enzinc, Salient Energy, Eos Energy Enterprises, ZAF Energy Systems, Gelion, UniEnergy Technologies, Green Zinc Batteries, FreeWire Technologies, Battery Associates, Energizer Holdings, Energous Corporation, Primus Power, Aquion Energy, and others. |
Key Segment |
By Product Type, By End-Use Sector, and Region |
Major Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East &, Africa |
Purchase Options |
Request customized purchase options to meet your research needs. Explore purchase options |
 Segmentation Analysis
Segmentation Analysis
The global zinc ion battery market is segmented based on product type, end-use industry, and region.
Based on product type, the global zinc ion battery industry is divided into zinc-mn battery, zinc-chloride battery, zinc-carbon battery, zinc-silver battery, zinc-nickel battery, and zinc-air battery. The ‘zinc-mn battery' segment leads the global market due to its brilliant environmental safety, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for grid-scale power storage. They are widely adopted in stationary applications, such as renewable energy integration and backup power systems. Their natural chemistry and high stability make them greatly suitable for early commercial deployments and research.
Based on end-use industry, the global zinc ion battery market is segmented into consumer electronics, LED lighting, automotive, and others. The ‘consumer electronics’ segment registers a substantial market share. Devices such as hearing aids, remote controls, medical wearables, and wireless keyboards utilize zinc-based batteries due to their eco-friendliness, low cost, and safety. The drive towards non-flammable and sustainable battery options in personal gadgets is boosting the adoption in the domain.
 Regional Analysis
Regional Analysis
- North America to witness significant growth over the forecast period
The Asia Pacific held a dominant share of the global zinc ion battery market, driven by the strong presence of battery manufacturing hubs, rural electrification projects, and a growing demand for low-cost energy storage. The Asia Pacific is a leader in battery production, with nations such as South Korea, China, India, and Japan dominating the industry in terms of battery producers and research and development centers.
China alone accounted for over 70 percent of the global battery cell market in the previous year. This infrastructure benefit extends to the pilot production and research and development of zinc-ion batteries, offering APAC a strong competitive edge in supply chain integration and innovation.
Additionally, several APAC nations have large rural populations with limited access to the grid. Zinc-ion batteries are cost-effective, low-maintenance, well-suited, and safe for telecom and solar lighting applications in such regions. According to the Asian Development Bank, more than 100 million individuals in Southeast Asia lack access to reliable electricity, creating a significant demand for decentralized power solutions, including zinc-ion solutions.
Furthermore, Asia Pacific's emphasis on high-volume applications and cost-sensitive markets is well-suited for zinc-ion battery properties. India's demand for low-cost power storage in microgrids (solar) is expected to rise by 28% annually by 2030, thus increasing interest in alternatives to lithium-ion batteries.
North America is expected to grow considerably, registering a second-leading share in the zinc ion battery industry. This growth is attributed to the higher demand for long-duration and safe storage solutions, the presence of research institutions and innovative startups, as well as supportive regulatory environments.
The United States' energy storage sector is notably expanding, with grid-scale installations projected to reach 30 GW annually by 2030. Zinc-ion batteries are examined for their aqueous (non-flammable) electrolytes, making them highly suitable for safety-sensitive use cases, such as renewable grid storage and residential backup systems.
Additionally, North America is home to prominent innovators such as Eos Energy Enterprises, Urban Electric Power, and Salient Energy. These companies are producing commercial-scale technologies for stationary power storage. Collaborations with institutions like Argonne National Laboratory, MIT, and the University of California accelerated research and development in zinc-based battery chemistries.
Moreover, states like New York and California have imposed orders for decarbonization and long-duration energy storage, fueling utility demand for zinc-ion solutions. For instance, New York's (CLCPA) Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act aims for 6 GW of power storage by 2030, offering opportunities for affordable and safe zinc-based batteries.
 Competitive Analysis
Competitive Analysis
The key players profiled in the global zinc ion battery market are:
- Zinc8 Energy Solutions
- Urban Electric Power
- Enzinc
- Salient Energy
- Eos Energy Enterprises
- ZAF Energy Systems
- Gelion
- UniEnergy Technologies
- Green Zinc Batteries
- FreeWire Technologies
- Battery Associates
- Energizer Holdings
- Energous Corporation
- Primus Power
- Aquion Energy
 Key Market Trends
Key Market Trends
- Improvements in cathode materials and electrolytes:
Ongoing research and development are fueling innovations in zinc-ion chemistry, particularly in hybrid electrolytes and manganese-based cathodes. Innovations such as dual-salt aqueous electrolytes and gel-based electrolytes are enhancing the life cycle, energy density, and dendrite suppression. These improvements are helping zinc-ion batteries approach the performance of lithium-ion batteries in mid-energy applications.
- Growing interest in non-toxic and sustainable batteries:
With the growing demand for eco-friendly substitutes, zinc-ion batteries are gaining prominence because they utilize recyclable, non-toxic, and abundant materials, such as water-based electrolytes and zinc. This trend aligns with the universal move towards green supply chains and ESG compliance, particularly in off-grid power systems and consumer electronics.
The global zinc ion battery market is segmented as follows:
 By Product Type Segment Analysis
By Product Type Segment Analysis
- Zinc-Mn Battery
- Zinc-Chloride Battery
- Zinc-Carbon Battery
- Zinc-Silver Battery
- Zinc-Nickel Battery
- Zinc-Air Battery
 By End-Use Sector Segment Analysis
By End-Use Sector Segment Analysis
- Consumer Electronics
- LED Lighting
- Automotive
- Others
 By Regional Segment Analysis
By Regional Segment Analysis
- North America
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- France
- The UK
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Australia
- Southeast Asia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- The Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Egypt
- Kuwait
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Industry Major Market Players
- Zinc8 Energy Solutions
- Urban Electric Power
- Enzinc
- Salient Energy
- Eos Energy Enterprises
- ZAF Energy Systems
- Gelion
- UniEnergy Technologies
- Green Zinc Batteries
- FreeWire Technologies
- Battery Associates
- Energizer Holdings
- Energous Corporation
- Primus Power
- Aquion Energy
Frequently Asked Questions

Copyright © 2024 - 2025, All Rights Reserved, Facts and Factors


